5.3 BIM Management
5.3.0 General
The BIM teams shall maximize BIM capability to meet project goals. BIM managers will attend project kick‐off meetings to understand MDOT MAA project goals and the scope of work. BIM Managers will then interpret these into BIM requirements and uses for the project to define the necessary members of the project BIM team. The BIM team will manage model development, submissions of the models, and documentation throughout the project phases. The Design BIM Manager has the responsibility for the design BIM Execution Plan (BxP).
5.3.1 BIM Roles, Responsibilities, and Expertise
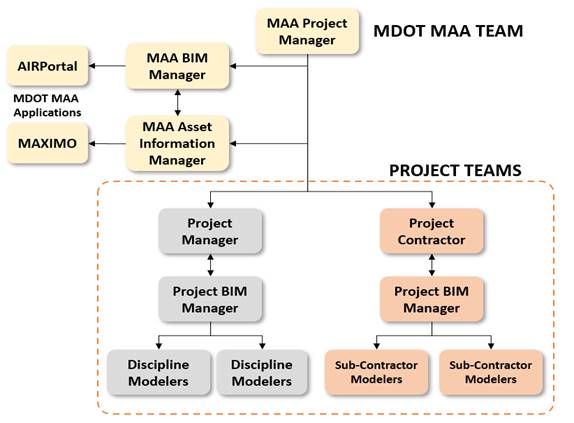
The consultant and contractor shall designate a BIM Manager responsible for BIM execution per the project scope of work (SOW). Team member roles are shown visually in Figure 5.3-1 and described in Table 5.3-1. Additional team members shall be assigned accordingly per the SOW, BIM Uses, and project complexity.

Figure 5.3-1 – BIM Teams
|
TABLE 5.3-1: BIM ROLES and RESPONSIBILITIES |
|||
|
MDOT MAA PM |
MDOT MAA PROJECT MANAGER – is the MDOT MAA representative with project management and oversight responsibilities on behalf of the MDOT MAA. The PM manages all aspects of the project to achieve the project goals. The PM works closely with the MDOT MAA BIM Manager on BIM schedule, deliverables, and data handovers. |
||
|
MDOT MAA CMi |
CONSTRUCTION MANAGER/INSPECTION – is the MDOT MAA representative during construction. This group will have oversight and review authority on BIM deliverables and the BxP per the SOW. |
||
|
MDOT MAA BIM Manager |
MDOT MAA BIM MANAGER – The MDOT MAA BIM Manager reviews and provides oversight on BIM requirements and deliverables. |
||
|
MDOT MAA Cx |
COMMISSIONING TEAM – A Commissioning team, if used, may request the model or model data for the commissioning process. |
||
|
A/E - DESIGN BIM TEAM |
GC - CONSTRUCTION BIM TEAM |
||
|
Design BIM Manager |
Construction BIM Manager |
||
|
Manages the use of the MDOT MAA Revit Template; provides oversight of model structure, development, and integration of discipline models; determines model/s information; maintains construction documentation, quality, submissions, and team collaboration |
Overall execution and use of BIM and construction documentation for the development of Shop models, constructability reviews, quantity take-off, and the As-Built information. |
||
|
Discipline Modelers |
Major disciplines modeling teams with the expertise to develop these models and provide analysis as needed per the project SOW |
Fabrication Modelers |
Sub-contractors’ BIM modelers managed by the Construction BIM Manager. Use the Design Intent model or other approved tools for fabrication. |
|
BIM Use Modelers Rendering, Animation, Public Presentations Separate team members may be assigned as a visualization task coordinator, estimator, LEED analyst per the SOW. Reports to the Design BIM Managers |
BIM Use Modelers Different teams may supply schedule (4D), estimating, (5D), and construction logistics visualizations tasks per the SOW. Teams report to Construction BIM Manager |
||
|
QA-QC – Model Management A separate team member may be designated as QA/QC task coordinator for model and data checking, model integration, and other multi-disciplinary activities. Reports to the Design BIM Manager. |
QA-QC – Model Management A separate team member may be designated as QA/QC task coordinator supporting the As-built model, data checking, model integration, and other multi-disciplinary activities. Reports to the Construction BIM Manager. |
||
5.3.1.1 BIM Manager (Consultant or Contractor) Expertise and Responsibilities
The BIM Manager shall have an in-depth technical knowledge of Revit modeling and structure, project delivery, and BIM processes. They can manage teams and convey instructions to designers and other modelers. BIM Managers shall have experience interpreting what BIM uses to meet project goals for the BxP creation and updates for the project. BIM Managers:
A. Ensure compliance with MDOT MAA BIM standards and manage QC program
B. Develop, maintain, update, and provide clarifications to the BxP
C. Manage model creation and review across discipline teams or trades during construction
D. Participate in project meetings for BIM review.
E. Lead and facilitate BIM meetings
F. Manage and coordinate team modelers
G. Verify geo‐references in all associated discipline models
H. Schedule periodic design coordination and construction coordination reviews
I. Manage submissions
J. Manage 2D Drawing, and BIM derived information production
K. Develop submission packages for design or construction handover to MDOT MAA and other parties
5.3.1.2 Discipline, BIM Users, and Fabrication Modelers
BIM teams require multiple areas of expertise. Discipline modelers are trained professionals in the discipline combined with BIM expertise. BIM Use modelers have additional software expertise that makes use of the Revit model.
A. Have professional expertise in the discipline to be modeled
B. Ability to review multiple discipline models for coordination and review
C. Object creation and best practice expertise for project use
D. Ability to derive and create documentation views and details from the model
E. Understand and adhere to standards
F. Fabrication modelers can utilize design intent models for fabrication through Revit or other fabrication software
G. BIM Use modelers use the model for analysis, rendering, animation, or other required uses beyond Revit capabilities
5.3.2 Project Kick-Off Meeting – BIM Participation
The MDOT MAA BIM Manager will work with the design team to define project BIM Uses and the model development strategy based upon MDOT MAA standards to achieve project goals. The BIM team must be aware of the downstream contractor, and MDOT MAA BIM uses to develop their model/s accordingly.
A. The MDOT MAA BIM Manager shall attend regular project review meetings and facilitate model uses to support MDOT MAA decision processes.
B. Regular BIM team meetings will be held to maintain the modeling schedule, model coordination, and quality control.
5.3.3 BIM Execution Plan (BxP) Development
Projects have different characteristics based upon scope, contract type, project type, assets, and type of construction, which illustrates why a common BIM package for all MDOT MAA projects is not possible. The BxP identifies and documents the model uses on the project, its structure, and responsible parties. It details the schedule for BIM development, LOD progression, model coordination activities, model structure, and required asset data. The BxP is a deliverable per Section 5.4, Table 5.4-1. The BxP provides the following information:
A. Project information
B. BIM goals & uses
C. Each project member’s role, staffing, and competency, contact information
D. BIM process and strategy
E. BIM exchange protocol and submittal format
F. BIM data requirements including additions to the MDOT MAA data naming conventions for new instances
G. Collaboration and discipline model referencing procedures for shared models
H. Quality control plan
I. Technology infrastructure & software used
5.3.3.1 BIM Execution Plan (BxP) Templates
There are two templates available to use for the MDOT MAA BxP:
A. MDOT MAA BxP_Template 1 – can be used for all size projects; composed of 2 separate files as follows:
1. MDOT_MAABxP_Template 1.docx
2. MDOT_MAABxP_Part2 LODMatrix_Attributes Parameters.xlsx
B. MDOT MAA BxP_Template 2 – typically used for smaller, simple projects
1. MDOT MAA BxP_Template 2.xlsx
Consultants shall confirm with the MDOT MAA BIM Manager, which template to use based on the complexity of the project.
5.3.3.2 BIM Execution Plan (BxP) Phases
The BxP documents the technical coordination of the model across teams. BxP development has two stages: the Design BxP and the Construction Phase BxP. Consultants and contractors must submit a BxP for their phase of the project for approval. The Design BxP is a contract deliverable as per Section 5.4, Table 5.4-1. As a contract deliverable, it provides documentation about the project BIM use and is a tool supporting post-project model use.
On DBB projects, the Design BxP is provided to the contractor. The contractor builds upon the Design BxP by adding additional information for the construction phase, which becomes the Construction Phase BxP.
On CMAR projects, the consultant and CM team jointly prepare the BxP. This combined plan is also called a Project Execution Plan (PxP).
5.3.4 BIM Uses
BIM Uses identify modeling tasks for the project, responsible parties, LOD, referenced standards, and the desired outcomes. BIM Uses are defined in the BxP for the design and construction phases. Below is a table of MDOT MAA recognized BIM Uses. Others may be added to the BxP.
|
TABLE 5.3-1: BIM USES for MDOT MAA |
PARTICIPANTS |
||||||
|
No. |
BIM USES |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
A/E |
GC CMAR |
CMi |
Cx |
MAA |
|
BIM Uses 1-17 by MDOT MAA Document all BIM Uses in the project BxP |
|||||||
|
1 |
Existing Conditions Modeling |
The model developed from field measurements, existing docs, and laser scanning to produce an accurate existing conditions model. The A/E and the contractor (GC or CMAR) are individually responsible for implementing any process or technology required to field-verify existing conditions needed to perform their contractual obligations. |
X |
X |
|
|
X |
|
2 |
A/E - Model Authoring |
Various discipline models developed for project design, analysis, and construction documentation |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
3 |
Visualization Animations |
3D model views developed to more realism supporting stakeholder understanding, public reviews, and decision-making processes |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
4 |
Space Program Validation |
Quantify space in the model for variations from project space requirements and codes |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
5 |
Fire Safety Review |
Model review of fire suppression system and alarm with the architectural model for interactive FM and Fire System reviews. |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
6 |
Design Analysis |
Analysis of design per scope of work, required egress plan, vertical circulation coordination, energy, and others as required in the SOW |
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
7 |
Coordination Reviews |
In-depth reviews of design for coordination. Use Navisworks, Revizto, or Solibri Model Checker for “Clash Detection” and data requirements |
X |
X |
|
|
X |
|
8 |
Quantity Take-Off Reports |
Reporting on areas, volumes, square footages, objects, and material quantities supporting analysis, validation, procurement, estimating, and building system analysis |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
9 |
Phasing-Modeling (4D) |
Use model phasing tools to show design phases for design planning and scheduling |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
10 |
Logistics Modeling |
Modeling and representative views or animations supporting site planning, material and equipment handling, traffic patterns, etc. |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
11 |
Construction Sequencing |
4D or views showing construction phases and project development over time |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
12 |
3D Trade Coordination |
Use of model checking and “clash - conflict resolution” to verify model/s coordination – A Clash Resolution report is a deliverable |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
13 |
Facilities Data Turnover |
As-Built model LOD 300 with accurate data for FM. GC/CMAR will update the LOD 300 model with as-installed data |
X |
X |
X |
|
X |
|
14 |
Digital Layout |
Use of laser layout equipment for field layout of walls and other elements in the construction |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
15 |
Laser Scanning |
Use of laser scanning as a base to develop highly accurate existing models or to capture as-built conditions during construction |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
16 |
Digital Cx |
Commissioning (Cx) of the model for data integrity – Use of model in the field during commissioning to verify data |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
17 |
Analysis Reporting |
All types of analysis including energy, daylighting, sun studies, LEED, as needed to meet project scope |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
A/E= Architectural Engineer, GC – General Contractor or CMAR, CMi = Construction Manager inspection Cx= Commissioning Team |
|||||||