5.1 Introduction to BIM
5.1.0 General
The MDOT MAA Building Information Modeling (BIM) Standards identify BIM-based modeling requirements for Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall (BWI Marshall) and Martin State (MTN) Airports projects. The model deliverable provides an “As Constructed” deliverable to MAA for configuration management, operations, and maintenance. The MDOT MAA recognizes the National BIM Standards definition for BIM:
“BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. BIM is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility, forming a reliable basis for decisions during its lifecycle, and defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition.” -National Institute of Building Sciences
This document is for design and construction service providers. MDOT MAA project consultants shall understand how the requirements affect their roles, project delivery, and deliverables. MDOT MAA assumes the reader has skills and knowledge of CAD and BIM project workflows, modeling methods, derived construction documentation, and the standard industry terms used in this document.
This standard, as part of the MDOT MAA Planning and Engineering Guidelines & Standards (PEGS), provides the basis for CAD, GIS, and BIM for MDOT MAA projects. Section 5.1.6 Referenced MDOT MAA Documents and National Standards contains other referenced standards.
|
TABLE 5.1-1: ACRONYMS in DOCUMENT |
|
|
3D |
Geometry in BIM representing building elements or assemblies |
|
4D |
Time sequencing of construction |
|
ASCE |
American Society of Civil Engineers |
|
ADM |
AIRPortal Document Manager |
|
A/E |
The terms A/E (architect-engineer) designer and consultant are interchangeable. |
|
BAS |
Building Automation Systems |
|
BIM |
Building Information Model, Modeling, Management |
|
BIM Uses |
How the project team use the model during the project |
|
BxP |
BIM Execution Plan |
|
CAD |
Computer-Aided Design |
|
CDE |
Common Data Environment |
|
CIM |
Civil Information Modeling |
|
CMAR |
Construction Manager at Risk |
|
CM |
Configuration Management being MAA’s activity to use the Record model of a facility or portion of for the Common Data Environment. May be provided by MAA to support the scope of work controlled by MAA |
|
CMMS |
Computer Maintenance Management System – Maximo at MDOT MAA |
|
CO |
Change Orders |
|
COBie |
Construction Operations Building information exchange |
|
CSI |
Construction Specifications Institute |
|
Cx |
Commissioning |
|
DBB |
Design Bid Build |
|
DD |
Design Development |
|
EDI |
Electronic Data Interchange |
|
e-Transmit |
Electronic exchange process tool |
|
FAA |
Federal Aviation Administration |
|
Field |
Mobile access to documentation |
|
FFE |
Furniture, Fixtures, Equipment |
|
GC |
General Contractor |
|
GIS |
Geographic Information System – ESRI at MDOT MAA |
|
IFC |
Industry Foundation Classes |
|
LoD |
Level of Development – the geometric and data accuracy of the model elements |
|
NCS |
National CAD Standard |
|
Nora |
Notice of Recommended Award |
|
NTP |
Notice to Proceed |
|
NSF |
Net Square Footage |
|
MAA |
Maryland Aviation Administration |
|
MDOT |
Maryland Department of Transportation |
|
MEPFT |
Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing, Fire Protection & Telecom (The National CAD Standard “T” discipline includes security) |
|
pegs |
MDOT MAA Planning and Engineering Guidelines & Standards |
|
RFI |
Request for Information |
|
SOW |
Scope of Work |
|
XREF |
eXternally REFerenced file inserted in a current drawing using the AutoCAD “ATTACH” command. |
5.1.1 MDOT MAA INFORMATION MANAGEMENT STRATEGY
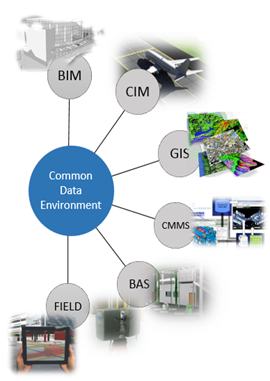
BIM adoption is part of the MDOT MAA multi-year strategy to develop a Common Data Environment (CDE) integrating planning, design, construction, operations, and facilities management information. The CDE will integrate BIM project data and geometry as “ground truth” into other applications (CMMS and GIS technologies) used as part of its operational workflows.
Figure 5.1-1. MDOT MAA’s Common Data Environment (CDE)
· BIM - Building Information Modeling
· CIM - Civil Information Modeling
· GIS - Geographic Information Systems
· CMMS - Computer Maintenance & Management System
· BAS - Building Automation Systems (sensors)
· FIELD - Mobile access to documentation

Figure 5.1-1- Common Data Environment
5.1.2 BIM Benefits and Goals
BIM is a process requiring standards, modeling strategy, and planning to maximize the benefits throughout the project lifecycle. It is necessary to “Begin with the End in Mind.” Benefits accrue throughout the project lifecycle into asset management and operations. MDOT MAA’s goal is to work with teams that maximize BIM benefits (see Figure 5.1-2) on projects and manage the demands of airport construction.
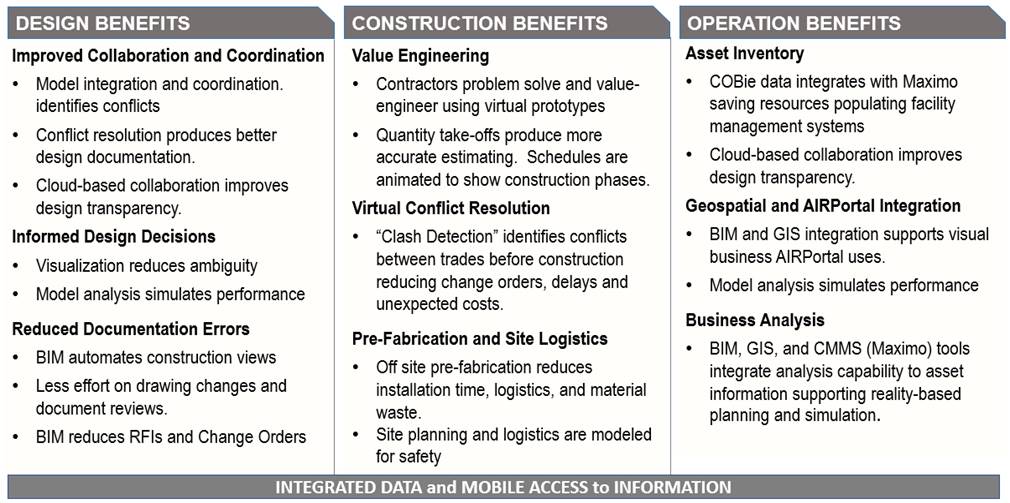
Figure 5.1-2- BIM Benefits
5.1.3 When to Use BIM on MDOT MAA Projects
Not all design and construction projects will require BIM. However, all interiors and facility projects, regardless of size, shall use BIM, and the model shall be a deliverable.
Table 5.1.2 is used by MDOT MAA to determine when a project requires BIM, which depends upon the project type, complexity, size, and cost. The use of BIM on a project will be outlined within the project scope of work, RFP, and reflected in the project deliverables. If a design team chooses to use BIM as their preferred design process, then follow the MDOT MAA BIM Standard which specifies Revit as the BIM authoring tool
|
TABLE 5.1-2: MDOT MAA BIM PROJECT MATRIX |
|||||
|
PROJECT TYPES |
BIM USE |
REQUIREMENTS |
BIM DELIVERABLES |
||
|
DESCRIPTION |
BxP |
CLASH |
|||
|
MDOT MAA Studies |
Optional at discretion of MDOT MAA |
Schematic model, design options, reports, visualization. |
No |
No |
TBD by MDOT MAA based upon SOW. Any model developed becomes a deliverable |
|
Architectural Design to 30% |
Required |
Some projects are ended at 15%-30%. If preliminary modeling is required follow the BIM Standards. LOD 200 – 300 and BIM Uses |
Yes |
Yes |
BxP, 30% model, 30% documents |
|
Small Projects - <500,000 |
Optional at discretion of MDOT MAA |
Small area,single or few disciplines - BIM if specified in SOW process |
Yes, if BIM |
Yes, if BIM |
60-100% model, documents, As-Built documents. Record model, DWGs |
|
Projects > $500,000 construction cost |
Required |
BIM per MDOT MAA Standards |
Yes, if BIM |
Yes, if BIM |
60-100% model deliverables, As-Built documents, Record model. |
|
New Construction |
Required modeling and BIM Uses per SOW |
Major discipline models, construction documents, reports |
Yes |
Yes |
30-60-100% Model and Documents (PDF) during Design Conformed models after BID Project close-out As-Built documents, Revit Record model LOD 300 - 450 Navisworks model including Shop models DWG Floor Plans for GIS MAA Asset Spreadsheet (COBie based) |
|
Building Renovation |
|||||
|
Building Systems Replacement or Renovation |
Primary equipment in building system, Architecture, MEP |
||||
|
Building Permit Tenant Projects |
As required by MAA |
Per SOW |
Yes |
Recommended |
|
5.1.4 Model Terminology and Definitions
MDOT MAA uses the following modeling terms and modeling relationships throughout project execution (Figure 5.1-3).
5.1.4.1 Study Model – BIM Optional
MDOT MAA may require BIM (Revit) use for study reports. It may be necessary to analyze the design, document options, or illustrate study findings.
5.1.4.2 Existing Conditions Model – Revit
Not all projects have existing facility information. At the beginning of a project, MDOT MAA may provide a model as part of existing documentation. If not, then the consultant shall produce a model to support the project scope of work.
A. Creating a Model of Existing Conditions
The consultant will use the MDOT MAA Revit template for model creation. Define the Level of Development (LOD) of model elements in the BIM Execution Plan (BxP). Laser scanning may be used as a basis for the model.
B. Receiving an Existing Condition Model from MDOT MAA
MDOT MAA may provide a model of the project area. The model LOD and accuracy will be confirmed at the MDOT MAA BIM/GIS Kick-off meeting. Document further model development in the BxP.
5.1.4.3 Design Intent Model – Revit
The Design Intent model is developed throughout the design phases. It is the basis for project collaboration, coordination, analysis, stakeholder reviews, and decisions. Most elements are LOD 300, others LOD 350 - 400 based on project requirements. The LOD matrix, part of the BxP, identifies an item LOD. Teams resolve discipline model conflicts periodically, as stated in the BxP. MDOT MAA reviews all model submissions for standards compliance. The 100% Design Intent model and derived construction documentation shall be coordinated and free of significant element conflicts and errors.
MDOT MAA will review and provide written comments on the various model submissions (documented in the BxP) for standards compliance. Comments requiring model changes will be updated for the following model submission and be compliant for the Bid process. Models and construction documentation are project deliverables per Section 5.4, Table 5-4.1.
5.1.4.4 Bid Model – Revit
The Bid model, provided by MDOT MAA to bidders, is the revised 100% Design Intent model. Responses to Bidder’s questions/comments submitted to MDOT MAA and design modifications or clarifications are issued as Addenda during the Bid process.
Bid models are created and submitted for DBB projects only. CMAR projects do not have a Bid phase.
5.1.4.5 Conformed Model – Revit
The Conformed model is the Bid model with all addenda incorporated by the design consultant. The winning contractor will receive the model after the initial NTP at a model handover meeting.
Conformed models are created and submitted for DBB projects. CMAR projects have an “Issued For Construction” model which is the final/100% Design Intent model with all addenda incorporated.
5.1.4.6 Construction Model – Revit and Navisworks
The Conformed model is a basis for additional construction modeling. This work provides detail and information for construction through shop modeling, constructability reviews, and product data. Construction BIM Uses will be documented in the BxP.
Navisworks is an approved tool for construction and shop model integration, constructability reviews, and clash detection. The Navisworks model is a final deliverable.
A. Construction Model – Revit
The contractor will use the Revit Conformed model as a basis for construction modeling.
B. Construction Model – Navisworks
The contractor will use Navisworks to integrate Revit modeling with shop models for clash detection and coordination. The Navisworks reports are provided to MDOT MAA, showing clash issues and resolution. The Navisworks model is updated with as-built information and is a deliverable as per Section 5.4, Table 5.4-1.
5.1.4.7 As-Built Drawings - Navisworks Model and.DWG Drawings
The contractor regularly provides as-built information to the design consultant to produce the Record model (Revit). Contractor supplied .dwg drawings may be required per the SOW. Dwg files shall conform to the layers defined in PEGS V1, Chapter 3 CAD Standards Layers within the MDOT MAA Revit template. Other layers may be added based upon project content. These layers shall be identified in the BxP. The Navisworks model deliverable contains the approved shop models, as-built data, and additional LOD detail.
5.1.4.8 Record Model – Revit and COBie Spreadsheet
The Record model is the Conformed model updated with as-built information supplied by the contractor. The Record model is LOD 300 or higher per element. Joint reviews of as-built conditions will facilitate knowledge transfer.
The COBie spreadsheet, per project SOW, is a model export providing asset data (building systems and equipment data) required by the MDOT MAA.
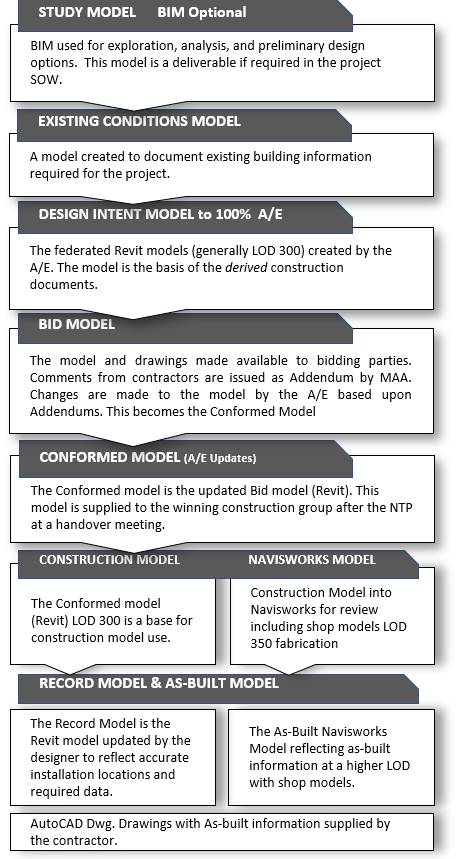
Figure 5.1-3 - MDOT MAA BIM Models
5.1.5 Model Progression by Contract Method
MDOT MAA uses Construction Manager at Risk (CMAR) and Design, Bid, Build (DBB) contracts on projects. These contracting methods must be determined at project inception as they alter model progression and handoff between parties.
5.1.5.1 Construction Manager at Risk (CMAR) BIM Model Progression
CMARs provide preconstruction services, collaboratively work with the design consultant, and maximize BIM, project cost, and schedule. A joint BxP created by the consultant and CMAR documents the services to be provided. The consultant updates model submissions with the CMAR and MDOT MAA comments during the project. These projects do not have a Bid model. The final/100% Design Intent model is developed collaboratively by the team with Addenda issued as necessary to support efficient construction procurement and delivery. The resulting documents are the Issued For Construction set and model.
Once construction begins, the CMAR serves as the project’s general contractor, constructing the project with company crews or subcontracted trades. The CMAR retains the responsibility for monitoring design—coordinating any design changes, advising the owner on any design modifications, and coordinating approval of shop drawings with the consultant. During construction, the CMAR provides as-built updates and equipment data for Record model creation. The as-built Navisworks (350-400) model and .dwg drawings per SOW are deliverables. The design consultant creates the Record model using the submitted as-builts.
5.1.5.2 Design, Bid, Build (DBB) BIM Model Progression
The Design BIM Manager shall submit the Design Intent model for MDOT MAA review at each design phase. The reviewed and updated 100% Design Intent model becomes the Bid model set. Bid models and the derived construction documents are part of the DBB project Bid package. The bidding contractors are provided the Bid models during the Bid process. Comments and model issues are submitted to MDOT MAA. MDOT MAA will address comments via addenda. This updated model becomes the Conformed model, which is provided to the winning contractor (GC) after NTP at a model handover meeting.
The contractor shall supply as-built information to the consultant to update the Record model (Revit). The As-Built model (Navisworks LOD 350 - 400) and CADD (.dwg) files reflecting as-built information are deliverables. The CAD drawings (.dwg) shall conform to PEGS V1, Chapter 3 CAD Standards, reflecting as-built conditions.
5.1.6 Referenced MDOT MAA Documents and National Standards
The MDOT MAA Planning and Engineering Guidelines & Standards (PEGS) contain the current design, CAD, and GIS guidelines for projects. This BIM document references these standards to decrease redundancy and conflicts. Introducing BIM on projects does not negate the requirements identified in these standards. Additional referenced standards include:
|
TABLE 5.1-3: ADDITIONAL REFERENCED STANDARDS |
|
MDOT MAA GIS Data Standards Utilities Supplement |
|
MDOT MAA Data Quality Standards |
|
MDOT MAA Data Security Standards |
|
MDOT MAA Building & Space Naming, Identification, Addressing, and Measurement Standard |
|
MDOT MAA Planning and Engineering Guidelines & Standards (PEGS) |
|
MDOT MAA Asset Management Standard |
|
BIM RELATED STANDARDS |
|
MDOT MAA Revit template |
|
National BIM Standards – National Institute of Building Sciences (NIBS) |
|
COBie (Construction Owner Building Information Exchange) - NIBS |
|
OmniClass - Construction Specification Institute (CSI) |
|
BIMForum Level of Development (LOD) - Associated General Contractors (AGC) |
|
|
5.1.7 Access to Documentation and Templates
The MDOT MAA provides consultants access to content through AIRPortal. https://www.airportal.maa.maryland.gov. Relevant content is available on the landing page and does not require a login. MAA MDOT will provide the information if it is not currently on AIRPortal.
|
TABLE 5.1-4: CONTENT AVAILABLE THROUGH AIRPortal |
|
Linetypes |
|
Symbols |
|
Logos |
|
MDOT MAA Additional Topographic Symbols |
|
Layer Template – X000‐Geom.dwg |
|
MDOT MAA Planning and Engineering Guidelines & Standards |
|
MDOT MAA Signage Symbols |
|
Plot Styles (ctb) |
|
Standards Borders |
|
Standards Title Block, Index Sheets |
|
BIM Execution Plan Template |
|
MDOT MAA Revit Template |
|
MDOT MAA BIM Standard |
|
MDOT MAA Asset Management System Data Delivery Standards |
5.1.8 Approved BIM Software
|
TABLE 5.1-5: SOFTWARE USE |
APPROVED APPLICATION NAME |
|
BIM Authoring Tool |
Autodesk Revit (Architecture, MEP, Structure) |
|
CIM Authoring Tool |
Autodesk Civil 3D |
|
Model Checking Tool |
Navisworks, Autodesk Model Checkers, Solibri, Revizto |
|
Drawing Submissions |
e‐Transmit |
|
Document Review |
Bluebeam and Autodesk Design Review |
|
Collaboration Tools |
BIM 360 Design, Docs, Build |
MDOT MAA uses Autodesk™ Revit software as its primary BIM authoring application. Other BIM authoring tools require MDOT MAA approval. Secondary tools for Revit, such as library management (UNIFY or others) or BIM 360 Design for collaboration, are part of the service providers' BIM environment documented in the project BIM Execution Plan (BxP).
5.1.9 BIM and Data Ownership
MDOT MAA shall have unlimited rights to all information and materials developed under a contract and furnished to the MDOT MAA, including all reports and listings, and all other items about the work and services according to its agreements, including any copyright. Unlimited rights under its contracts are rights to use, duplicate, or disclose data and information, in whole or part in any manner and for any purpose whatsoever without compensation to or approval from Contractor. The MDOT MAA will at all reasonable times have the right to inspect the work and will have access to and the right to make copies of the items mentioned above. All digital files and data, and other products generated under MDOT MAA contracts shall become the property of the MDOT MAA.
5.1.10 Waiver of BIM Standards Requirements
If a modification to a BIM requirement is in the best interest of the project, then a written waiver identifying the change, purpose, and alternative shall be submitted via email to the MDOT MAA for approval. Include the MDOT MAA PM on the email. After approval, document the changes in the BxP. E-mail address maapegsstandards@bwiairport.com.
5.1.11 Quality Assurance
The efficiency of the BIM process and the value of the construction documents depends upon model structure, level of development (LOD) accuracy, periodic model review and clash detection resolution, and quality control procedures. Plans, sections, elevations, essential details, schedules are derived from the model and have minimal 2D drafting. The consultant is responsible for seeing that all electronic files are compliant with all applicable MDOT MAA Standards and Guidelines.
The MDOT MAA Revit template is the base file for design. The Design BIM Manager shall periodically review the federated discipline models for conflicts using Navisworks, Autodesk Model Checker, or Solibri model checking tools. The clash/conflict reports are project deliverables. These reports will include the conflict type, number of specific conflicts, and the schedule for resolution by the design team.
Construction documentation is derived from conflict checked and resolved models with a minimum of 2D drafting on details. Schedules are reported from the model. The MDOT MAA BIM Manager will review model submissions for standards adherence, conflicts, and errors. The 100% model shall be free of reported errors and clashes before accepting the 100% model.